1
/
of
4
Changsha Rich Nonferrous Metals Co.,Ltd
Germanium Metal Ge Lumpy Ge Ingot 99.999% Pure
Germanium Metal Ge Lumpy Ge Ingot 99.999% Pure
Regular price
$35.00
Regular price
$0.00
Sale price
$35.00
Unit price
/
per
100 in stock
Couldn't load pickup availability
1. Basic characteristics of germanium metal:
- Element symbol: Ge
- Atomic number: 32
- Metal type: Metalloid
- Appearance: Lustrous, hard, grayish-white
- Melting point: 938.25 °C
- Boiling point: 2,830 °C
- Purity: Ge 99.999%

2. Discovery of germanium metal:
- Discovered by the German chemist Clemens Winkler in 1886.
- Germanium is primarily obtained as a byproduct of zinc ore processing.
3. Occurrence and distribution of germanium metal:
- Germanium is relatively rare in the Earth's crust and is not found as a free element.
- It is mainly found in the form of zinc ores and extracted during processing.
4. Applications of germanium metal:
- Electronics and semiconductor industry: Germanium is a semiconductor material used in electronic devices and integrated circuits.
- Fiber optics: Germanium is used as a dopant in optical fibers to control the refractive index and enhance light transmission.
- Infrared optics: Germanium is transparent to infrared radiation, making it useful in infrared spectroscopes and thermal imaging devices.
- Catalysts: Germanium compounds can serve as catalysts in certain chemical reactions.
- Alloying agent: Germanium can be used as an additive in certain metal alloys to improve their properties.
5. Limitations and alternative materials:
- The applications of germanium have been somewhat limited due to the development of alternative materials and technologies.
- Demand for germanium has decreased with advancements in technology.
- Germanium metal still finds niche applications in specific electronic devices and optical applications.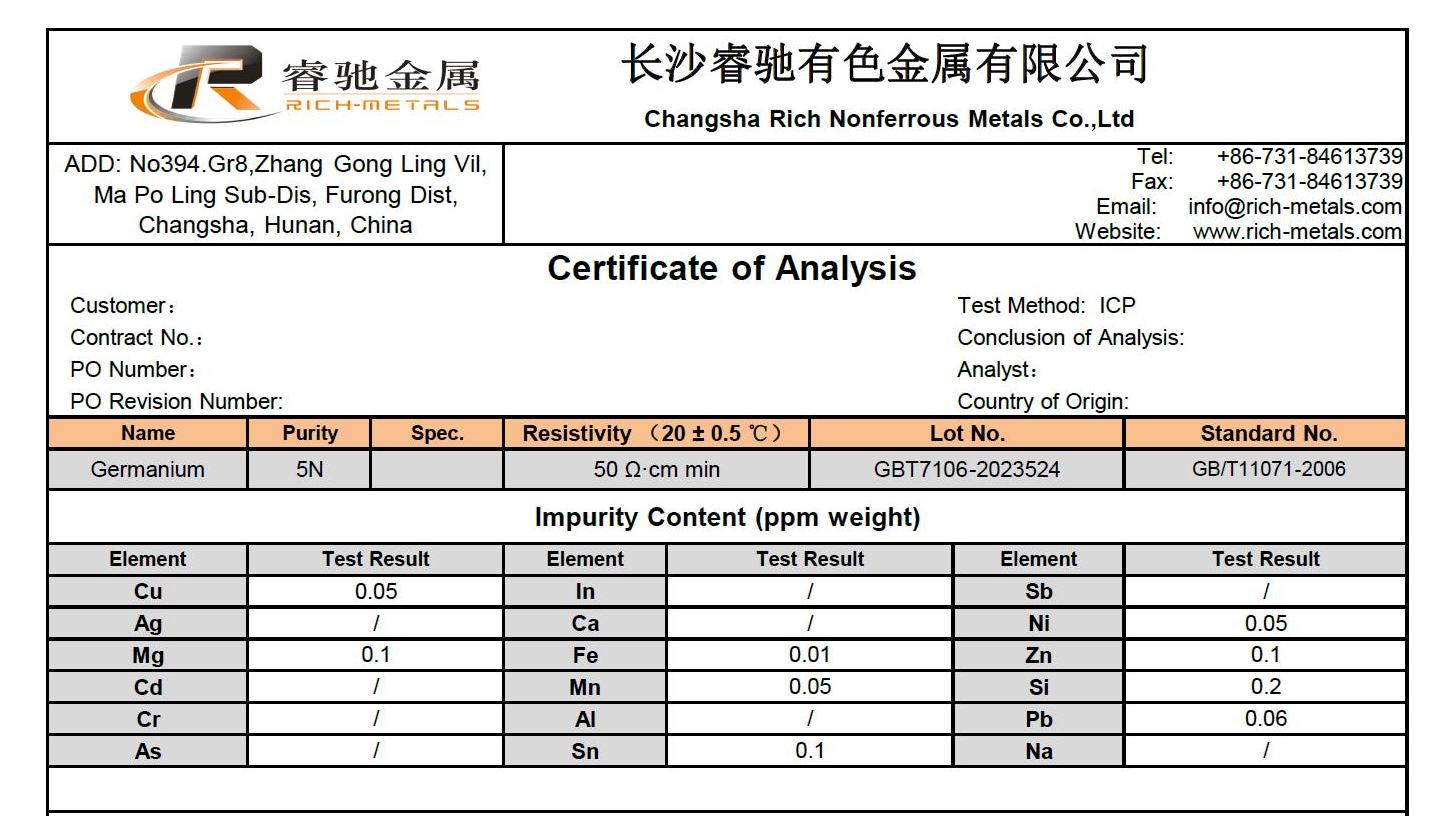
- Element symbol: Ge
- Atomic number: 32
- Metal type: Metalloid
- Appearance: Lustrous, hard, grayish-white
- Melting point: 938.25 °C
- Boiling point: 2,830 °C
- Purity: Ge 99.999%

2. Discovery of germanium metal:
- Discovered by the German chemist Clemens Winkler in 1886.
- Germanium is primarily obtained as a byproduct of zinc ore processing.
3. Occurrence and distribution of germanium metal:
- Germanium is relatively rare in the Earth's crust and is not found as a free element.
- It is mainly found in the form of zinc ores and extracted during processing.
4. Applications of germanium metal:
- Electronics and semiconductor industry: Germanium is a semiconductor material used in electronic devices and integrated circuits.
- Fiber optics: Germanium is used as a dopant in optical fibers to control the refractive index and enhance light transmission.
- Infrared optics: Germanium is transparent to infrared radiation, making it useful in infrared spectroscopes and thermal imaging devices.
- Catalysts: Germanium compounds can serve as catalysts in certain chemical reactions.
- Alloying agent: Germanium can be used as an additive in certain metal alloys to improve their properties.
5. Limitations and alternative materials:
- The applications of germanium have been somewhat limited due to the development of alternative materials and technologies.
- Demand for germanium has decreased with advancements in technology.
- Germanium metal still finds niche applications in specific electronic devices and optical applications.

Share












